Page 8 - GUIAS ESC ESH 2018
P. 8
8 ESC/ESH Guidelines
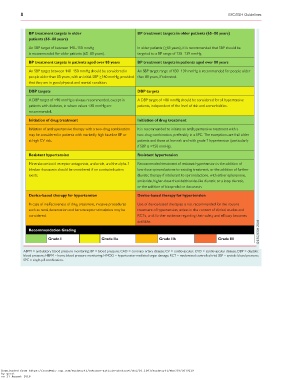
BP treatment targets in older BP treatment targets in older patients (65–80 years)
patients (65–80 years)
An SBP target of between 140–150 mmHg In older patients (>_65 years), it is recommended that SBP should be
is recommended for older patients (65–80 years). targeted to a BP range of 130–139 mmHg.
BP treatment targets in patients aged over 80 years BP treatment targets in patients aged over 80 years
An SBP target between 140–150 mmHg should be considered in An SBP target range of 130–139 mmHg is recommended for people older
people older than 80 years, with an initial SBP >_160 mmHg, provided than 80 years, if tolerated.
that they are in good physical and mental condition.
DBP targets DBP targets
A DBP target of <90 mmHg is always recommended, except in A DBP target of <80 mmHg should be considered for all hypertensive
patients with diabetes, in whom values <85 mmHg are patients, independent of the level of risk and comorbidities.
recommended.
Initiation of drug treatment Initiation of drug treatment
Initiation of antihypertensive therapy with a two-drug combination It is recommended to initiate an antihypertensive treatment with a
may be considered in patients with markedly high baseline BP or two-drug combination, preferably in a SPC. The exceptions are frail older
at high CV risk. patients and those at low risk and with grade 1 hypertension (particularly
if SBP is <150 mmHg).
Resistant hypertension Resistant hypertension
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, amiloride, and the alpha-1 Recommended treatment of resistant hypertension is the addition of
blocker doxazosin should be considered if no contraindication low-dose spironolactone to existing treatment, or the addition of further
exists. diuretic therapy if intolerant to spironolactone, with either eplerenone,
amiloride, higher-dose thiazide/thiazide-like diuretic or a loop diuretic,
or the addition of bisoprolol or doxazosin.
Device-based therapy for hypertension Device-based therapy for hypertension
In case of ineffectiveness of drug treatment, invasive procedures Use of device-based therapies is not recommended for the routine
such as renal denervation and baroreceptor stimulation may be treatment of hypertension, unless in the context of clinical studies and
considered. RCTs, until further evidence regarding their safety and efficacy becomes
available.
Recommendation Grading
Grade I Grade IIa Grade IIb Grade III
ABPM = ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; BP = blood pressure; CAD = coronary artery disease; CV = cardiovascular; CVD = cardiovascular disease; DBP = diastolic
blood pressure; HBPM = home blood pressure monitoring; HMOD = hypertension-mediated organ damage; RCT = randomized controlled trial; SBP = systolic blood pressure;
SPC = single-pill combination.
Downloaded from https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339/5079119
by guest
on 27 August 2018