Page 10 - GUIAS ESC ESH 2018
P. 10
10 ESC/ESH Guidelines
.
3 Definition, classification, and . . 3.2 Classification of blood pressure
.
epidemiological aspects of . . . .
hypertension Classification of BP
3.1 Definition of hypertension
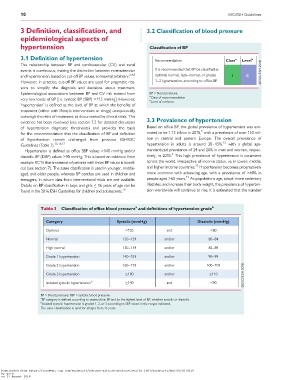
Recommendation Class a Level b
The relationship between BP and cardiovascular (CV) and renal
events is continuous, making the distinction between normotension It is recommended that BP be classified as
and hypertension, based on cut-off BP values, somewhat arbitrary. 2,4,8 optimal, normal, high–normal, or grades I C
However, in practice, cut-off BP values are used for pragmatic rea- 1–3 hypertension, according to office BP.
sons to simplify the diagnosis and decisions about treatment.
Epidemiological associations between BP and CV risk extend from BP = blood pressure.
a Class of recommendation
very low levels of BP [i.e. systolic BP (SBP) >115 mmHg]. However,
b
Level of evidence.
‘hypertension’ is defined as the level of BP at which the benefits of
treatment (either with lifestyle interventions or drugs) unequivocally
outweigh the risks of treatment, as documented by clinical trials. This
3.3 Prevalence of hypertension
evidence has been reviewed (see section 7.2 for detailed discussion
of hypertension diagnostic thresholds) and provides the basis Based on office BP, the global prevalence of hypertension was esti-
5
for the recommendation that the classification of BP and definition mated to be 1.13 billion in 2015, with a prevalence of over 150 mil-
of hypertension remain unchanged from previous ESH/ESC lion in central and eastern Europe. The overall prevalence of
Guidelines (Table 3). 15,16,17 hypertension in adults is around 30 - 45%, 12 with a global age-
Hypertension is defined as office SBP values >_140 mmHg and/or standardized prevalence of 24 and 20% in men and women, respec-
5
diastolic BP (DBP) values >_90 mmHg. This is based on evidence from tively, in 2015. This high prevalence of hypertension is consistent
multiple RCTs that treatment of patients with these BP values is benefi- across the world, irrespective of income status, i.e. in lower, middle,
12
cial (see section 7). The same classification is used in younger, middle- and higher income countries. Hypertension becomes progressively
aged, and older people, whereas BP centiles are used in children and more common with advancing age, with a prevalence of >60% in
12
teenagers, in whom data from interventional trials are not available. people aged >60 years. As populations age, adopt more sedentary
Details on BP classification in boys and girls <_16 years of age can be lifestyles, and increase their body weight, the prevalence of hyperten-
found in the 2016 ESH Guidelines for children and adolescents. 18 sion worldwide will continue to rise. It is estimated that the number
a
Table 3 Classification of office blood pressure and definitions of hypertension grade b
Category Systolic (mmHg) Diastolic (mmHg)
Optimal <120 and <80
Normal 120–129 and/or 80–84
High normal 130–139 and/or 85–89
Grade 1 hypertension 140–159 and/or 90–99
Grade 2 hypertension 160–179 and/or 100–109
Grade 3 hypertension >_180 and/or >_110
b
Isolated systolic hypertension >_140 and <90
BP = blood pressure; SBP = systolic blood pressure.
a
BP category is defined according to seated clinic BP and by the highest level of BP, whether systolic or diastolic.
b
Isolated systolic hypertension is graded 1, 2, or 3 according to SBP values in the ranges indicated.
The same classification is used for all ages from 16 years.
Downloaded from https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339/5079119
by guest
on 27 August 2018