Page 52 - GUIAS ESC ESH 2018
P. 52
52 ESC/ESH Guidelines
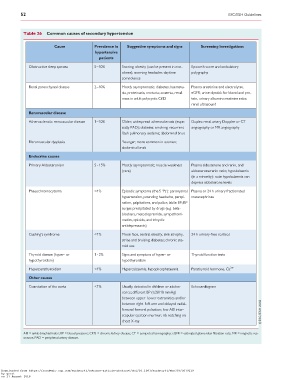
Table 26 Common causes of secondary hypertension
Cause Prevalence in Suggestive symptoms and signs Screening Investigations
hypertensive
patients
Obstructive sleep apnoea 5–10% Snoring; obesity (can be present in non- Epworth score and ambulatory
obese); morning headache; daytime polygraphy
somnolence
Renal parenchymal disease 2–10% Mostly asymptomatic; diabetes; haematu- Plasma creatinine and electrolytes,
ria, proteinuria, nocturia; anaemia, renal eGFR; urine dipstick for blood and pro-
mass in adult polycystic CKD tein, urinary albumin:creatinine ratio;
renal ultrasound
Renovascular disease
Atherosclerotic renovascular disease 1–10% Older; widespread atherosclerosis (espe- Duplex renal artery Doppler or CT
cially PAD); diabetes; smoking; recurrent angiography or MR angiography
flash pulmonary oedema; abdominal bruit
Fibromuscular dysplasia Younger; more common in women;
abdominal bruit
Endocrine causes
Primary Aldosteronism 5 - 15% Mostly asymptomatic; muscle weakness Plasma aldosterone and renin, and
(rare) aldosterone:renin ratio; hypokalaemia
(in a minority): note hypokalaemia can
depress aldosterone levels
Phaeochromocytoma <1% Episodic symptoms (the 5 ‘Ps’): paroxysmal Plasma or 24 h urinary fractionated
hypertension, pounding headache, perspi- metanephrines
ration, palpitations, and pallor; labile BP; BP
surges precipitated by drugs (e.g. beta-
blockers, metoclopramide, sympathomi-
metics, opioids, and tricyclic
antidepressants)
Cushing’s syndrome <1% Moon face, central obesity, skin atrophy, 24 h urinary-free cortisol
striae and bruising; diabetes; chronic ste-
roid use
Thyroid disease (hyper- or 1 - 2% Signs and symptom of hyper- or Thyroid function tests
hypothyroidism) hypothyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism <1% Hypercalcaemia, hypophosphataemia Parathyroid hormone, Ca 2þ
Other causes
Coarctation of the aorta <1% Usually detected in children or adoles- Echocardiogram
cence; different BP (>_20/10 mmHg)
between upper–lower extremities and/or
between right–left arm and delayed radial-
femoral femoral pulsation; low ABI inter-
scapular ejection murmur; rib notching on
chest X-ray
ABI = ankle-brachial index; BP = blood pressure; CKD = chronic kidney disease; CT = computed tomography; eGFR = estimated glomerular filtration rate; MR = magnetic res-
onance; PAD = peripheral artery disease.
Downloaded from https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339/5079119
by guest
on 27 August 2018