Page 47 - GUIAS ESC ESH 2018
P. 47
ESC/ESH Guidelines 47
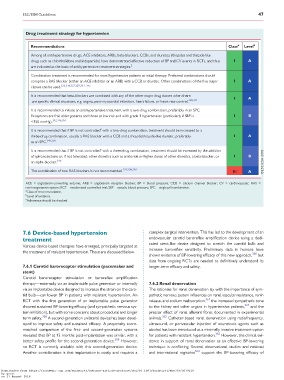
Drug treatment strategy for hypertension
Recommendations Class a Level b
Among all antihypertensive drugs, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, CCBs, and diuretics (thiazides and thiazide-like
drugs such as chlorthalidone and indapamide) have demonstrated effective reduction of BP and CV events in RCTs, and thus I A
are indicated as the basis of antihypertensive treatment strategies. 2
Combination treatment is recommended for most hypertensive patients as initial therapy. Preferred combinations should
comprise a RAS blocker (either an ACE inhibitor or an ARB) with a CCB or diuretic. Other combinations of the five major I A
classes can be used. 233,318,327,329,341–345
It is recommended that beta-blockers are combined with any of the other major drug classes when there
I A
are specific clinical situations, e.g. angina, post-myocardial infarction, heart failure, or heart rate control. 300,341
It is recommended to initiate an antihypertensive treatment with a two-drug combination, preferably in an SPC.
Exceptions are frail older patients and those at low risk and with grade 1 hypertension (particularly if SBP is I B
<150 mmHg). 342,346,351
c
It is recommended that if BP is not controlled with a two-drug combination, treatment should be increased to a
three-drug combination, usually a RAS blocker with a CCB and a thiazide/thiazide-like diuretic, preferably I A
as an SPC. 349,350
c
It is recommended that if BP is not controlled with a three-drug combination, treatment should be increased by the addition
of spironolactone or, if not tolerated, other diuretics such as amiloride or higher doses of other diuretics, a beta-blocker, or I B
310
an alpha-blocker.
The combination of two RAS blockers is not recommended. 291,298,299 III A
ACE = angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB = angiotensin receptor blocker; BP = blood pressure; CCB = calcium channel blocker; CV = cardiovascular; RAS=
renin-angiotensin system; RCT = randomized controlled trial; SBP = systolic blood pressure; SPC = single-pill combination.
a
Class of recommendation.
b
Level of evidence.
c
Adherence should be checked.
.
7.6 Device-based hypertension . . . complex surgical intervention. This has led to the development of an
treatment . . . . endovascular carotid baroreflex amplification device using a dedi-
Various device-based therapies have emerged, principally targeted at . . . cated stent-like device designed to stretch the carotid bulb and
the treatment of resistant hypertension. These are discussed below. . . . . . . increase baroreflex sensitivity. Preliminary data in humans have
360
but
shown evidence of BP-lowering efficacy of this new approach,
7.6.1 Carotid baroreceptor stimulation (pacemaker and . . . . . data from ongoing RCTs are needed to definitively understand its
longer-term efficacy and safety.
stent) . . .
Carotid baroreceptor stimulation or baroreflex amplification . . .
therapy—externally via an implantable pulse generator or internally . . . 7.6.2 Renal denervation
via an implantable device designed to increase the strain on the caro- . . . The rationale for renal denervation lay with the importance of sym-
tid bulb—can lower BP in patients with resistant hypertension. An . . . pathetic nervous system influences on renal vascular resistance, renin
RCT with the first generation of an implantable pulse generator . . . release, and sodium reabsorption, 361 the increased sympathetic tone
showed sustained BP-lowering efficacy (and sympathetic nervous sys- . . . to the kidney and other organs in hypertensive patients, 361 and the
tem inhibition), but with some concerns about procedural and longer . . . pressor effect of renal afferent fibres documented in experimental
term safety. 358 A second-generation unilateral device has been devel- . . . animals. 362 Catheter-based renal denervation using radiofrequency,
oped to improve safety and sustained efficacy. A propensity score- . . . ultrasound, or perivascular injection of neurotoxic agents such as
matched comparison of the first- and second-generation systems . . . alcohol has been introduced as a minimally invasive treatment option
revealed that BP at 12 months post-implantation was similar, with a . . . . for patients with resistant hypertension. 363 However, the clinical evi-
better safety profile for the second-generation device. 359 However, . . . dence in support of renal denervation as an effective BP-lowering
no RCT is currently available with this second-generation device. . . . technique is conflicting. Several observational studies and national
Another consideration is that implantation is costly and requires a . and international registries 364 support the BP-lowering efficacy of
Downloaded from https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339/5079119
by guest
on 27 August 2018